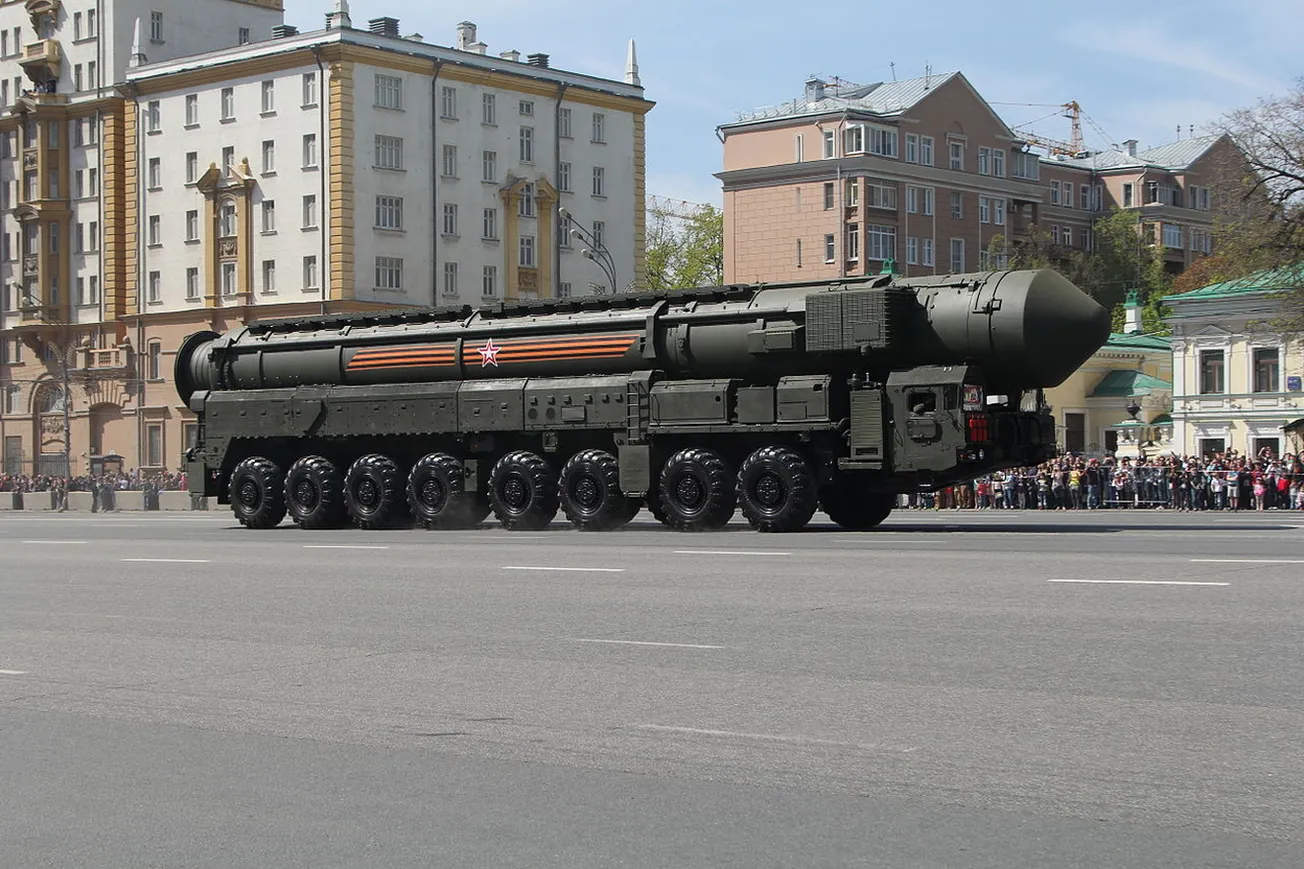
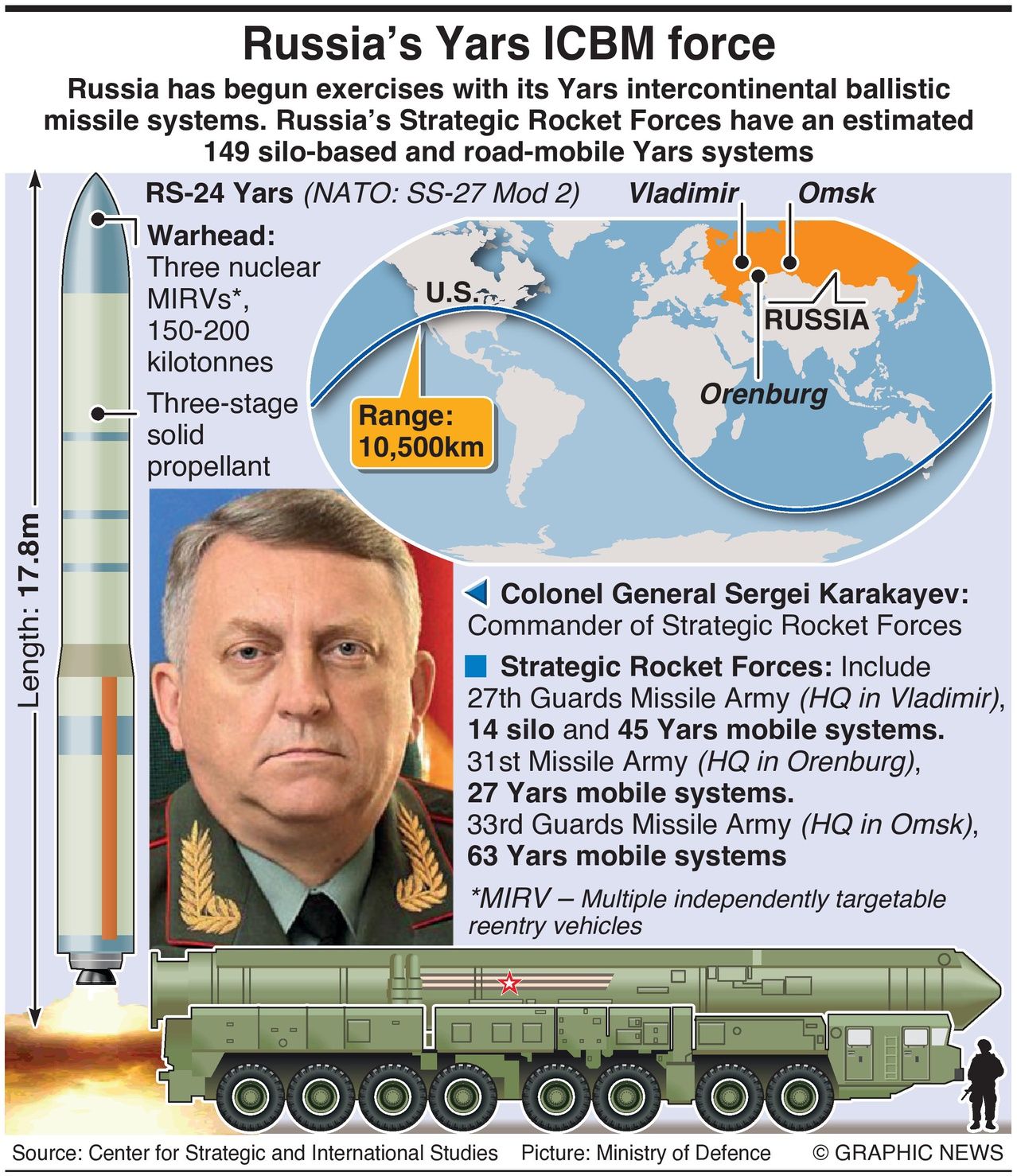
Russia has begun exercises with its Yars intercontinental ballistic missile systems. Russia’s Strategic Rocket Forces have an estimated 149 silo-based and road-mobile Yars systems.
“In total, more than 3,000 military personnel and about 300 pieces of equipment are involved in the exercises,” the Ministry of Defence said in a statement on the Telegram messaging service.
Commanded by Colonel General Sergei Karakayev, the Strategic Rocket Forces include three missile armies equipped with 14 silo-based and 135 road-mobile RS-24 Yars (NATO designation: SS-27 Mod 2) missile systems: the 27th Guards Missile Army (headquarters in Vladimir), the 31st Missile Army (Orenburg), and the 33rd Guards Missile Army (Omsk).
The RS-24 Yars -- introduced into service in July 2010 -- is an upgraded version of the Topol-M ballistic missile. The ICBM can carry three multiple independently targetable nuclear warheads (MIRVs) designed to evade missile defense systems up to a range of 10,500km.
In January 2021, the Ministry of Defence of the Russian Federation published information on the missile range and other characteristics of the newest Yars-S mobile ground-based missile system.
The caliber of the rocket is 1.86m, and the length is 17.8m. The launch mass of the missile is 46,000kg, and the payload is 1,250kg.
The rocket travels in a sealed transport and launch container, maintaining a constant temperature and humidity.
As of early 2020, Russia’s Strategic Rocket Forces had as many as 320 operationally deployed missiles, which could carry up to 1181 warheads. The number of deployed warheads is likely smaller as Russia would have otherwise exceeded the New START limit on the total number of deployed warheads.